
Bluffton University Nature Preserve, Bluffton, OH
Bioimages home (click on an image to enlarge)
view
this page in its intended navigation context
Southern Great Lakes Forests
(WWF
ecoregion
NA0414)

Bluffton University Nature Preserve,
Bluffton, OH
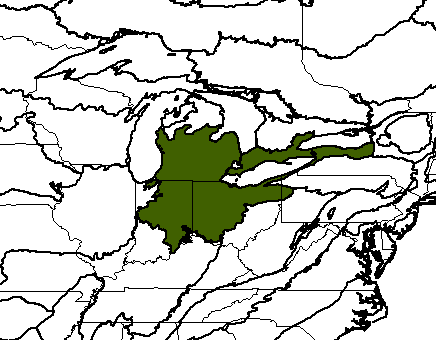
Source of bioregions data:
Olson, D. M. and
E. Dinerstein. The Global 200: Priority ecoregions for global conservation. (PDF
file) Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden 89:125-126.
Distinctiveness (1=highest,4=lowest): 4
(nationally important)
Some rare ecological phenomena exist, such as dune systems associated with the
Great Lakes and wetland remnants.*
Conservation Status (1=most endangered, 5=most
intact): 1 (critical)
Virtually none of the habitat in this ecoregion remains intact.
Agriculture, and industrial and urban development have heavily impacted this
area. Remaining habitat patches are tiny and severely fragmented. Immense
wetlands have been drained and converted to agriculture.*
 Acer
saccharum
Acer
saccharum Fagus
grandifolia
Fagus
grandifolia Tilia
americana
Tilia
americana Carya
species
Carya
species
 Ulmus
spp.
Ulmus
spp.
 Fraxinus
spp.
Fraxinus
spp. Acer
rubrum (red maple)
Acer
rubrum (red maple)
Some associated habitats








* Ricketts, T.H., E. Dinerstein, D.M. Olson, C.J. Loucks, et al. (1999) Terrestrial Ecoregions of North America: A Conservation Assessment. World Wildlife Fund - United States and Canada. Island Press, Washington, D.C. pp. 164-166.
Except as noted, images copyright 2002-2004 Steve Baskauf - Terms of use